What you need to know after NAET Treatments
- Wash your hands after treatment. If unable to wash with water then rub hands together for 20-30 seconds.
- If you experience any adverse reaction after a NAET treatment seek help from a primary care physician or call 911 if reaction is severe.
- DRINK water frequently before and after treatment.
- If you experience any of the following you will need to balance your energy by rubbing the 10 gates in a clockwise direction every two hours on your own at home while you are AWAKE.
- Any discomfort during the 25 hour avoidance period after the NAET (crying spells, anxiety, etc.)
- You can not avoid the item (such as it is inside you or you need the item for medicinal reasons)
- You accidentally eat item
- You are exposed to the treated item (touch, smell or breath item)
NAET Gate Points
Move from each point in a clockwise direction starting with right hand and moving up right arm, down left arm, down left leg, up right leg, end at right hand where you began.
- With hand 60 seconds at each point
- With acustim massager 30 seconds at each point
- With 635 nm laser 15 seconds each point
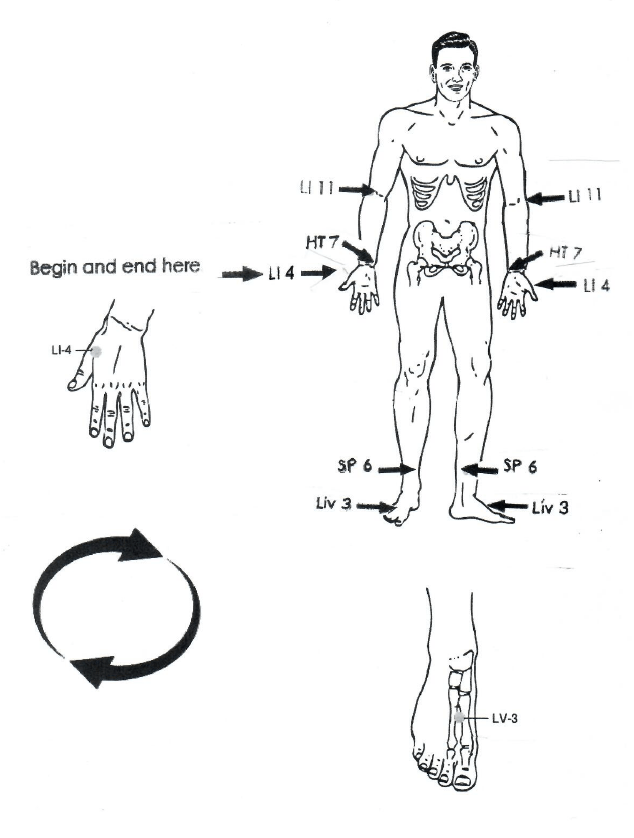
- Start gate point stimulation on right back hand on LI 4, between thumb and index finger
- Move to right wrist HT 7, point lies where wrist bends down from 5th digit (pinky)
- Move to right crease in arm LI 11, between lateral crease in arm and elbow
- Move to left crease in arm LI 11
- Move to left wrist HT 7
- Move to left back of hand L1 4
- Move to left lower leg SP 6, three finger widths above medial malleolus (ankle bone on inside of leg)
- Move to left foot LV 3, in the depression between first and second tarsal bones (big toe and second toe)
- Move to right foot LV 3
- Move to right lower leg SP 6
- Finish on right back of hand LI 4
For at least 25 hours after treatment of each of the basic 17 mixes patients will need to go through a temporary avoidance period. The following is information on items that need to be avoided following each treatment.
For a full list of avoidance foods and more information please refer to “The NAET Guide Book 11th edition” found at NAET.com or on Amazon. Highly sensitive people should be cleared for white rice first and can eat white rice during the 25 hours following each treatment.
1. BBF: no need to avoid anything
2. Egg Mix:
- Avoid all food products containing eggs or chicken including breads, broths, cakes, cookies, crackers, custards, food baked with eggs, fried food using egg batter, mayonnaise, pancakes, pastries, pies, protein drinks make with egg, puddings, salad dressings, soups, thick sauces, vitamins with egg components.
- Also avoid touching or coming near five feet in distance: birds, hair or skin products with egg in the ingredients, feather comforters and pillows
- It is ok to eat fruits, vegetables, meat (other than chicken), beans, grains, rice, pastas (without egg)
3. Calcium Mix:
Avoid foods that contain more than 2% of the daily allowance of calcium such as:
- Dairy products: Milk, yogurt, cheese, and kefir
- Leafy green vegetables: Spinach, kale, collard greens, and broccoli
- Fortified foods: Certain cereals, plant-based milk alternatives (like almond or soy milk), and orange juice fortified with calcium
- Tofu: Tofu made with calcium sulfate
- Fish with bones: Canned salmon and sardines are examples of fish that are high in calcium due to their edible bones.
It is ok to eat foods that contain less than 2% of the daily recommended amount of calcium such as:
- Fruits like apples, bananas, and oranges.
- Vegetables such as lettuce, cucumbers, and bell peppers.
- Grains like white rice, pasta, and bread made from refined flour.
- Most nuts and seeds, except for almonds and sesame seeds, which have slightly higher calcium content.
- Oils, fats, and sugars, as they generally contain very little to no calcium.
- Beef, turkey, chicken (without bone), eggs (don’t touch egg shells)
4. Vitamin C Mix
Avoid foods that contain more than 2% of the daily recommended amount of vitamin C such as:
- Citrus fruits: Oranges, grapefruits, lemons, and limes
- Berries: Strawberries, raspberries, blueberries, and blackberries
- Kiwi fruit: Kiwi is a tropical fruit
- Bell peppers: Particularly red and green bell peppers
- Broccoli: This cruciferous vegetable is not only rich in fiber and other nutrients but also contains a significant amount of vitamin C.
- Brussels sprouts: Another cruciferous vegetable that is a good source of vitamin C.
- Tomatoes: Whether eaten fresh or in the form of tomato juice or sauce, tomatoes provide vitamin C.
- Leafy greens: Spinach, kale, and Swiss chard are examples of leafy greens with notable vitamin C content.
- Body lotions or cosmetics that contain citric acid.
- Avoid grasses, plants, trees, bushes, weeds, flowers, walking in the garden, sitting under fruit trees.
It is ok to eat foods that typically contain less than 2% of the daily recommended amount of vitamin C such as:
- Grains: Foods made from refined grains like white rice, white bread, and pasta.
- Fats and Oils: Cooking oils such as vegetable oil, olive oil, and canola oil generally contain very little vitamin C.
- Animal-based products: Meat, poultry, fish, and eggs are not significant sources of vitamin C.
- Dairy products: While dairy products like milk, cheese, and yogurt provide essential nutrients, they are not significant sources of vitamin C.
- Most processed and packaged foods: Snack foods, desserts, and processed meats usually contain minimal amounts of vitamin C unless fortified.
5. B Complex Mix
Avoid eating foods with more than 2% of vitamin B vitamins such as:
- Whole grains: Brown rice, oats, barley, quinoa and whole wheat
- Legumes: Lentils, beans, and peas
- Nuts and seeds: Sunflower seeds, pistachios, and pecans
- Dairy products: Milk, yogurt, and cheese
- Lean meats: Chicken, turkey, and lean cuts of beef
- Leafy greens: Spinach, kale, and collard greens
- Fish: Tuna, salmon, and trout
- Avocado
- Bananas
- Nuts and seeds: Almonds, peanuts, and sunflower seeds
- Eggs
- Sweet potatoes
- Legumes: Lentils, chickpeas, and black beans
- Fortified foods: Some cereals, plant-based milk alternatives, and nutritional yeast are fortified with vitamin B12
- Touching grasses, plants, trees, flowers, walking in gardens, etc.
It is ok to eat foods that typically contain less than 2% of the daily recommended amount of various B vitamins such as:
- Refined grains: White rice, white bread, and regular pasta are often lower in B vitamins compared to whole grains.
- Sugary snacks and desserts: Foods like candies, cakes, and cookies usually contain minimal B vitamins.
- Processed meats: Hot dogs, bacon, and deli meats may have lower levels of B vitamins compared to fresh, unprocessed meats.
- Highly processed foods: Packaged snacks, fast food items, and convenience meals often have limited B vitamin content due to extensive processing and added sugars, fats, and preservatives.
6. Sugar Mix:
- Avoid all forms of sugar, maple, honey, brown rice, whole grains, carrots, fruits, beets, milk, milk products, sauces, drinks, pre-packaged food with sugar, granola, syrups, salad dressings, juices, yogurt, canned fruits, canned baked beans, peanut butter, oatmeal, creamy salad dressings, toothpaste or any other item that contains sugar.
- It is ok to eat meats, grains, cooked vegetables, rice, lentils, avocado, cucumber, celery, cauliflower, asparagus, kale, lettuce, mushrooms, and nuts
7. Iron mix:
Avoid foods that contain more than 2% of the daily recommended amount of iron such as:
- Red meat: Beef, lamb, and pork
- Poultry: Chicken, turkey, and duck
- Fish and seafood: Shellfish like oysters, clams, and mussels
- Legumes: Beans, lentils, chickpeas, and peas
- Tofu and tempeh: soy-based products are rich in iron, especially if they’re fortified.
- Seeds: Pumpkin seeds, sesame seeds, hemp seeds, and flaxseeds
- Nuts: Almonds, cashews, and pine nuts
- Dark leafy greens: Spinach, kale, Swiss chard, and collard greens
- Fortified foods: Some breakfast cereals, bread, and plant-based milk alternatives are fortified with iron.
- Organ meats: Liver, kidneys, and heart
- Dark Chocolate
- Dried fruits like apricots, raisins, and prunes
- Avoid touching leather, avoid iron skillet or other iron cookware.
It is ok to eat foods that typically contain less than 2% of the daily recommended amount of iron such as:
- Dairy products: Milk, cheese, and yogurt generally contain minimal amounts of iron.
- Fruits: While fruits provide various essential nutrients, most fruits are not significant sources of iron.
- Vegetables: Many vegetables, such as carrots, cucumbers, and lettuce, contain only small amounts of iron.
- Grains: Foods made from refined grains like white rice, white bread, and pasta usually contain minimal iron compared to whole grains.
- Fats and oils: Cooking oils such as vegetable oil, olive oil, and canola oil typically contain very little iron.
- Sugary snacks and desserts: Foods like candies, cakes, and cookies usually contain negligible amounts of iron.
8. Vitamin A Mix:
Avoid Foods that contain more than 2% of the daily recommended amount of vitamin A such as:
- Liver: Beef liver, chicken liver, and other organ meats
- Meats: chicken, turkey, fish, lamb, beef
- Colorful vegetables and fruits such as sweet potatoes, carrots, mangos, cantaloupe, red bell peppers
- Leafy Greens: Spinach, kale, and Swiss chard
- Pumpkin: Rich in beta-carotene, pumpkin
- Winter Squash: Varieties like butternut squash and acorn squash
- Fish Liver Oils: Cod liver oil
- Dairy Products: Milk, cheese, and butter
- Eggs: Particularly the yolks
- Fortified cereals
It is ok to eat foods with less than 2% of vitamin A such as:
- Grains: Refined grains like white rice, white bread, crackers and pasta that have not been fortified
- Fats and oils: Cooking oils such as vegetable oil, olive oil, and canola oil
- Sugary snacks and desserts: Foods like candies, cakes, and cookies
- Beverages: Most beverages, including water, tea, and coffee, do not provide significant amounts of vitamin A unless they are fortified.
- Nonfat yogurt
- Sour cream
9. Mineral Mix:
- Do not use or touch mineral or tap water, root vegetables (onion, potato, carrots, turnips), fish and shellfish, pesticides, metal surfaces (wearing gloves is ok), metal jewelry, hair accessories with metal, metal utensils, metal cookware
- It is ok to eat cooked meat, cooked vegetables, apples, bananas, beans, berries, milk, salad, fruit, distilled water (prepare food in advance to avoid touching metal while cooking).
10. Salt Mix:
Avoid foods that contain more than 2% salt (sodium chloride) in them such as:
- Processed and cured meats: Items like bacon, ham, sausage, and deli meats often have high salt content due to the curing process.
- Canned soups and broths: Many commercially prepared soups and broths contain significant amounts of added salt for flavor and preservation.
- Salty snacks: Chips, pretzels, crackers, and other snack foods often have high levels of added salt.
- Processed cheese: Cheese spreads, cheese slices, and cheese dips may contain added salt for flavor and preservation.
- Condiments and sauces: Soy sauce, ketchup, barbecue sauce, and salad dressings can be high in salt.
- Pickled foods: Pickles, olives, and other pickled vegetables often contain high levels of salt as a preservative.
- Ready-to-eat meals: Frozen dinners, microwave meals, and packaged meals often have high salt content to enhance flavor and extend shelf life.
- Some fruits and vegetables such as: celery, romaine lettuce, watermelon, carrots, beets, artichoke, watercress, avocado, tomatoes, cabbage, cucumber, asparagus, pineapple
It is ok to eat foods that typically contain less than 2% salt (sodium chloride) such as:
- Fresh fruits and vegetables: Most fresh fruits and vegetables are naturally low in sodium unless they have been processed or canned with added salt.
- Plain grains: Unprocessed grains like rice, oats, quinoa, and barley are naturally low in sodium.
- Fresh meats and seafood: Fresh cuts of meat, poultry, and fish generally have low sodium content compared to processed or cured varieties.
- Plain dairy products: Milk, yogurt, and cheese without added flavorings or salt are low in sodium.
- Nuts and seeds: Raw nuts and seeds typically have minimal sodium content.
- Legumes: Beans, lentils, and peas are naturally low in sodium.
- Eggs: Eggs in their natural state contain very little sodium.
- Herbs and spices: Fresh and dried herbs, as well as spices without added salt blends, are naturally low in sodium.
11. Grain Mix (includes gluten):
- Avoid whole grains and items made from wheat, corn, rice, oat, rye, and barley.
- It is ok to eat vegetables, fruits, chicken, beef, and milk products.
12. Yeast Mix:
- Avoid brewer’s yeast, bakers yeast, and any foods containing these items.
- Ok to eat vegetables, nuts, quinoa, white rice, beef, chicken, fish, turkey, pork.
13. Stomach Acids:
Avoid foods with a pH below 6.9. These are considered mildly acidic to slightly acidic. Here are some examples:
- Most fruits: Many fruits fall within this pH range, including apples, oranges, strawberries, and grapes.
- Some vegetables: Vegetables such as tomatoes, carrots, potatoes and onions
- Dairy products: Some dairy products like yogurt and buttermilk and sharp cheeses
- Certain beverages: Some beverages like coffee, tea, beer, wine and fruit juices
- Fermented foods: Fermented foods like sauerkraut and pickles
- Some grains: Certain grains and grain products, such as whole grain bread and brown rice, bread, popcorn
It is ok to eat foods with a pH of 7.0 or higher are considered neutral or alkaline. Here are some examples:
- Water: Pure water has a neutral pH of 7.0.
- Most Vegetables: Many vegetables have a pH above 7.0, making them slightly alkaline. Examples include broccoli, cabbage, cauliflower, cucumbers, and leafy greens.
- Most Fruits: Most fruits also have a pH above 7.0. Examples include berries, melons
- Nuts and Seeds: Nuts and seeds tend to have a pH above 7.0. Examples include almonds, walnuts, peanuts, and sunflower seeds.
- Legumes: Legumes such as beans, lentils, and peas are generally slightly alkaline.
- Milk and Dairy Alternatives: Cow’s milk and many dairy alternatives, such as almond milk and soy milk, tend to have a pH above 7.0.
- Eggs: Eggs have a neutral pH of around 7.6 to 7.8.
- Quinoa
14. Base:
- Opposite of Acid. Don’t eat foods with ph of 7.0 or higher. Eat foods with ph lower than 7.0. See lists above.
15. Hormones:
- Avoid food from hormone fed or injected animals. Avoid stimulating hormones by avoiding hugging or kissing during 25 hours after treatment. Avoid treating during the menstrual period.
- You can eat milk substitutes and food without added hormones.
16. Organ Mix:
- Do not eat animal fat, organ meat, meat products (beef, chicken, turkey, and lamb).
- Ok to eat other food that are not meat
17. Vitamin K:
Avoid foods that contain more than 2% of the daily recommended amount of vitamin K such as:
- Leafy greens: Dark, leafy greens: kale, spinach, collard greens, Swiss chard, and mustard greens.
- Cruciferous vegetables: Vegetables like broccoli, Brussels sprouts, and cabbage
- Herbs: Fresh herbs such as parsley, cilantro, basil, and thyme
- Green vegetables: Green vegetables like asparagus, green beans, and green peas
- Lettuce: Different types of lettuce, including romaine lettuce and leaf lettuce
- Natto: A traditional Japanese food made from fermented soybeans
- Soybean oil: Soybean oil
- Avocado: Avocado
It is ok to eat foods that typically contain less than 2% of the daily recommended amount of vitamin K such as:
- Fruits: Most fruits, such as apples, bananas, oranges, and berries
- Grains: Foods made from refined grains, such as white rice, white bread, and pasta
- Meat and poultry: While meat and poultry
- Dairy products: Milk, cheese, yogurt, and other dairy products
- Fats and oils: Cooking oils like vegetable oil, olive oil, and canola oil
- Sugary snacks and desserts: Foods like candies, cakes, and cookies usually contain negligible amounts of vitamin K.
- Beverages: Most beverages, including water, tea, and coffee
Many of the foods that need to be temporarily avoided after a NAET treatment are the nutritious foods that after the avoidance period you are encouraged to eat and enjoy on a regular basis. Eating nutritious foods that are made by nature will help your body have the tools it needs to repair, restore, and thrive.